What Is Bitcoin Mining: How Does it Work, Proof of Work, Mining Hardware and More

As of late March 2022, Bitcoin value hit clocked in at $43,394.80 on the exchange market. This value is an indication of good tidings for the cryptocurrency. Over the years, there has been such a growing interest in the Bitcoin currency that its value has grown to resemble that of gold.
- The blockchain ledger keeps growing as transactions that have taken place in the network are constantly added to it.
- Transactions in the blockchain network are grouped into blocks that are linked together to form a chain of blocks, hence blockchain.
- Blockchain transactions are stored in chronological order marked by timestamps and hash functions.
- By this virtue, records stored in the blockchain network are permanent and immutable.
- Purchasing bitcoins on the exchange market
- Accepting bitcoin in exchange for goods and services
- Mining new bitcoins
Of these three, bitcoin mining is perhaps the most exciting option as it sends miners on a path to discovery. There is a caveat. Bitcoin mining can be quite taxing as it requires very high computing power to solve complex mathematical equations to verify transactions and add them to the blockchain digital ledger.
Simplilearn’s video tutorial explains the process of Bitcoin mining and the advantages of Bitcoin over traditional fiat currencies.
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first decentralized digital currency that allows peer-to-peer transfers without any intermediaries such as banks, governments, agents, or brokers, using the underlying technology of blockchain. Anyone around the world on the network can transfer Bitcoins to someone else on the network regardless of geographic location; you just need to just open an account on the Bitcoin network and have some Bitcoins in it, and then you can transfer those Bitcoins. How do you get Bitcoins in your account? You can either purchase them online or mine them.
Bitcoin can be used for online purchases and or as an investment instrument. Primarily it’s used to buy goods and services.
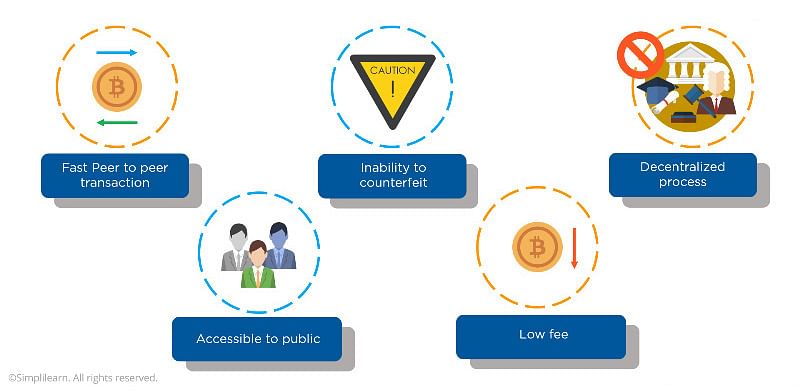
Bitcoin Advantages
Compared to traditional fiat currencies, assets can be transferred faster on the bitcoin network. The system also has lower transaction fees, because it’s decentralized and there are no intermediaries, and it is cryptographically secure—the identities of the sender and the receiver are kept hidden, and it is impossible to counterfeit or hack the transactions. Plus, all the information is available on a public ledger, so anyone can view the transactions.
What Is Blockchain?
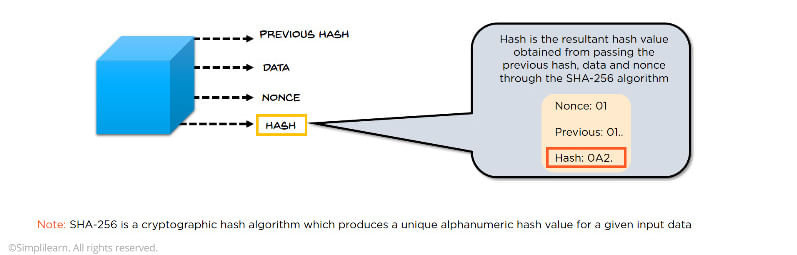
As mentioned, blockchain is the underlying technology of bitcoin. Blockchain is a public distributed ledger in which transactions are recorded in chronological order. Any record or transaction added to the blockchain cannot be modified or altered, meaning transactions are safe from hacking. A block is the smallest unit of a blockchain, and it is a container that holds all the transaction details. A block has four fields, or primary attributes:
- Previous hash: This attribute stores the value of the hash of the previous block, and that’s how the blocks are linked to one another.
- Data: This is the aggregated set of transactions included in this block—the set of transactions that were mined and validated and included in the block.
- Nonce: In a “proof of work” consensus algorithm, which bitcoin uses, the nonce is a random value used to vary the output of the hash value. Every block is supposed to generate a hash value, and the nonce is the parameter that is used to generate that hash value. The proof of work is the process of transaction verification done in blockchain.
- Hash: This is the value obtained by passing the previous hash value, the data and the nonce through the SHA-256 algorithm; it is the digital signature of the block.
SHA-256 is a cryptographic hash algorithm that produces a unique 256-bit alphanumeric hash value for any given input, and that is the unique feature of this cryptographic algorithm: Whatever input you give, it will always produce a 256-bit hash.
3 Concepts of Blockchain
To understand bitcoin mining, you have to first understand the three major concepts of blockchain.
- Public distributed ledger: A distributed ledger is a record of all transactions maintained in the blockchain network across the globe. In the network, the validation of transactions is done by bitcoin users.
- SHA-256: Blockchain prevents unauthorized access by using a hash function called SHA-256 to ensure that the blocks are kept secure. They are digitally signed. Their hash value, once generated, cannot be altered. SHA-256 takes an input string of any size and returns a fixed 256-bit output, and it is a one-way function—you cannot derive the reverse of the input reverse fully from the output (what you have generated).
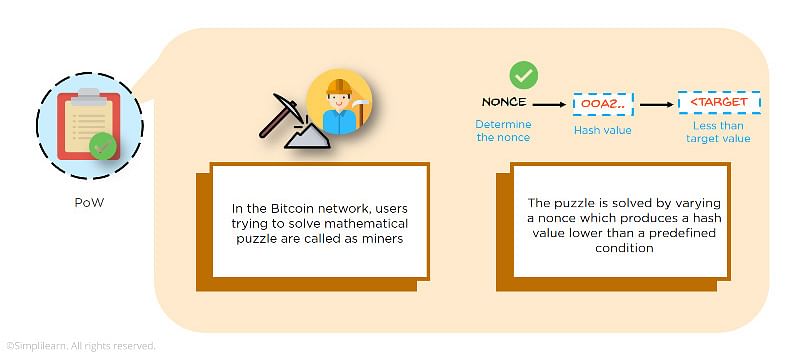
- Proof of work: In blockchain mining, miners validate transactions by solving a difficult mathematical puzzle called proof of work. To do that, the primary objective of the miner is to determine the nonce value, and that nonce value is the mathematical puzzle that miners are required to solve to generate a hash that is less than the target defined by the network for a particular block.
What Is Bitcoin Mining in Blockchain?
Bitcoin mining is the process by which Bitcoin transactions are validated digitally on the Bitcoin network and added to the blockchain ledger. It is done by solving complex cryptographic hash puzzles to verify blocks of transactions that are updated on the decentralized blockchain ledger. Solving these puzzles requires powerful computing power and sophisticated equipment. In return, miners are rewarded with Bitcoin, which is then released into circulation hence the name Bitcoin mining.
Bitcoin vs. Traditional Currencies
While both Bitcoin and traditional currency are similar in that both are a store of value, they differ in many ways. First things first, Bitcoin is the first and most recognized cryptocurrency – a digital currency that is secured by cryptography. Traditional currency, also referred to as fiat money, is a government-issued and regulated currency.
Some differences between Bitcoin and traditional currencies are illustrated in the table below.
Bitcoin |
Traditional Currency |
|
| Tangibility | It is a virtual currency and can only be used in its digital form | It is a physical currency in the form of notes and coins. However, we can use it in both physical and digital forms |
| Regulation | Issued through mining and controlled by a decentralized distributed network of computers | Issued and controlled by central government authorities, i.e., central banks. Owing to this, the traditional currency is the legal tender in the country governed by the issuing authority. |
| Governance | Governed by a consensus mechanism in which the majority rules | Purely governed by the central bank |
| Value | Value is backed by the trust of its users. The more users are willing to transact with Bitcoin, the more stable it becomes. | Value is determined by forces of supply and demand and is thus vulnerable to inflation |
| Supply | Capped at 21 million bitcoin | Fiat currency has no supply limit |
| Validation of transactions | Bitcoin transactions are validated using blockchain technology and so do not require an intermediary for validation | Transactions involve an intermediary such as a bank or a payment provider |
| Transaction fees | Minimal or no associated fees as intermediaries have been eliminated | Transactions attract considerable charges |
| Transaction time and speed | The transaction is almost always instantaneous or greatly depends on the network speed | Transactions may take time before verification or before they reflect on the system |
| Security | The concepts of decentralization, cryptography, and consensus guarantee a secure network and security of bitcoin transactions | Less secure as it can be negatively affected by fluctuations in government policies |
| Reversals | Bitcoin transactions cannot be charged back, reversed, or canceled | Chargebacks, reversals, and cancellations are commonplace with traditional currency transactions |
How Does Bitcoin Mining Work: Public Distributed Network, POW, The 64-Digit Hexadecimal Number (SHA-256 Algorithm)
Blockchain is a decentralized peer-to-peer network that has been hailed as highly secure and transparent, hence trustworthy. This is because records in the blockchain network are secured using timestamps and cryptographic hash functions in such a way that after being added to the ledger, it is almost impossible and impractical to alter the transactions. At the core of blockchain security is the absence of centralized control.
Here is a breakdown of what happens during bitcoin mining
-
The Mining Requirements
A bitcoin miner will first select their tools of the trade and set them up. These include:
- Hardware GPU (graphics processing unit), SSD for crypto mining, or ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit)
- Mining software
- A wallet
- Preferred mining pool (if one chooses pool mining option instead of solo mining)
Once all these are set up and the system fired up, it performs the mining process autonomously. Any other human involvement comes in the event of system or network failure, power outage, or regular system maintenance.
-
Elements of a Bitcoin Transaction
When a transaction is initiated in the bitcoin network, three elements are involved:
- A transaction input
- A transaction output
- The transaction amount
For every transaction input, a bitcoin mining software generates a unique cryptographic hash puzzle that is difficult to decode. The software then groups the number of transactions required to form a block into a Merkle tree.
-
The Merkle Tree and the SHA-256 Algorithm
A Merkle tree is a data structure of the hashes in a block and acts as a summary of all the transactions in the block. In the Merkle tree, hashes of individual transactions known as transaction IDs are paired repeatedly using the SHA-256 algorithm until only one hash identifies the entire tree. This hash is known as the Merkle root or root hash.
The Merkle tree enables the efficient verification of transactions in the bitcoin network.
-
The Block Header
The Merkle root, the identifier of a Merkle tree, is stored in the block header. The block header contains information about the block and includes the following components:
- The version number of the bitcoin software
- The hash of the previous block
- The Merkle root (root hash)
- Timestamp
- Cryptographic nonce
- The target
This is the information miners will use to solve the hash puzzle and add a block transaction.
-
Solving the Hash Puzzle
Miners must solve the hash puzzle by finding the hash below a given target through the difficulty requirement. The target, stored in the header, is expressed as a 67-digit number that will determine the mining difficulty based on the number of miners competing to solve a hash function. It is important to note that this difficulty adjusts after every 2016 blocks are created depending on how much time it took miners in the previous 2016 blocks to solve an equation. This also helps to maintain the rate at which transactions are appended in the blockchain at 10 minutes.
To solve the hash puzzle, miners will try to calculate the hash of a block by adding a nonce to the block header repeatedly until the hash value yielded is less than the target. Once a mining computer solves the puzzle, a new block is successfully created that is validated in the Bitcoin network after a consensus between the nodes has been reached. When a block is validated, the transactions bundled in it are verified and the block is added to the chain. As indicated above, this happens every 10 minutes.
As there will be many miners (systems) competing to solve the puzzle, the first miner to get the correct hash value earns a reward in Bitcoin. This process allows more Bitcoins in circulation.
Mining and Bitcoin Circulation
Bitcoin’s upper supply limit of 21 million bitcoin set by its source code by Satoshi Nakamoto, its inventor, is puzzling. However, experts have seen it as a huge advantage because the scarcity of supply breeds value and a stable price for the oldest crypto.
From the genesis Bitcoin block mined in 2009 with 50 bitcoins, more bitcoins have since been mined and released into circulation. Bitcoin mining ensures that blocks of transactions are created and stacked in the right order in a way that can be traced and proven mathematically. With the creation of blocks comes bitcoins as a reward, which increases the number of bitcoins in circulation.
Bitcoin architecture was structured ingeniously such that every 10 minutes, a block is discovered, and a fixed bitcoin award is offered for every block that is mined.
Prevention of Hacking
What if someone tries to hack the data? Blockchain, as the name implies, is a chain of blocks—let’s call the blocks A, B and C. Each block has solved a puzzle and generated a hash value of its own, which is its identifier. Now suppose a person tries to tamper with block B and change the data. The data is aggregated in the block, so if the data of the block changes, then the hash value that is the digital signature of the block will also change. It will therefore corrupt the chain after it—the blocks ahead of block B will all get delinked, because the previous hash value of block C will not remain valid.
| Interested to learn the Bitcoin Transaction Process? Enroll in the Blockchain Training Course and learn today! |
For a hacker to make the entire blockchain valid for the block B that has been changed, he or she would have to change the hash value of all the blocks ahead of block B. This would require a huge amount of computing power and is next to impossible. With this method, blockchain is non-hackable and prevents data modification.

Why Mine Bitcoin?
Let’s be straight: people primarily mine Bitcoin to earn profits. Other than that, people who are curious about this technology and how it works enjoy experimenting with this relatively new technology.
How Much Does a Miner Earn – Bitcoin Halving
Bitcoin halving refers to the splitting of block rewards into half to mean that miners’ reward for discovering a block is reduced by half. Halving exists to lower Bitcoin’s inflation rate and the rate at which new Bitcoins are released into circulation, keeping the price of Bitcoin stable. The halving event happens after every 210,000 blocks have been mined, which is roughly after every four years. The number of Bitcoins in circulation is calculated by the halving theory laid out by Satoshi Nakamoto in the Bitcoin protocol.
When Bitcoin was first launched, the reward for every block mined started at 50 Bitcoins. To date, three halving events have taken place, and the block reward went from 50 from 2009, 25 from 2012, 12.5 from 2016, to the current 6.25 BTC from 2020. The last Bitcoin halving event took place on May 11th, 2020.
By September 2021, 18.828 million of the 21 million Bitcoin cap had been mined and released into circulation, accounting for roughly 89.7% of all the Bitcoins to be mined.
The next Bitcoin halving event is expected to take place in the early months of the year 2024. Halving should continue until all blocks are mined, and the 21 million Bitcoin supply cap is attained sometime in 2140. After this, the Bitcoin miners will only earn from transaction fees.
What Do I Need to Mine Bitcoins?
Mining must have been a lot easier in the early days of its launch. As bitcoin and the blockchain concept were relatively new, mining was left to hobbyists on a discovery path. In fact, bitcoin’s inventor Nakamoto mined the genesis block on a basic CPU. As bitcoin continues to gain wider adoption, it has also succeeded in drawing keen interest from investors, miners, and companies harnessing cryptocurrency as a mode of payment for products and services. With this, mining has become a very competitive undertaking, and the hardware and software demands for bitcoin mining are also more sophisticated.
Today, bitcoin mining requires specialized tools, including:
- Hardware such as GPU (graphics processing unit), SSD for crypto mining, ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit), or the latest FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) chips. When purchasing mining hardware, it is important to consider two factors, their hash rate (performance) and electricity consumption.
- Mining software such as ECOS, BeMine, and Kryptex Miner
- A bitcoin wallet from which an individual performs bitcoin transactions
- Preferred mining pool (if one chooses pool mining option instead of solo mining)
Is Bitcoin Mining Profitable?
Figure 50 BTC block rewards every 10 minutes in the space of less competition, lower capital requirements, and lower running power and device maintenance costs.
Well, that was then when fewer miners enjoyed the monopoly. Mining is still considered a profitable venture, primarily because Bitcoin’s value is way higher today than it was then. However, competition is stiffer, and mining difficulty is greater.
What Does It Take to Run a Profitable Bitcoin Mining Venture?
-
Choice of Hardware
Bitcoin mining hardware performance is measured in terms of hash rate. Current new-generation ASIC miners produce 100 TH/s (trillion hashes per second) and cost somewhere between $8,000 – $10,000. Ordinary CPUs do not have the capacity to produce such fast hash rates.
-
Location
Developed nations may well have an edge when it comes to location because of the low cost of power. Bitcoin is quite power-intensive. It was estimated that one bitcoin transaction requires approximately 1,544 kWh of power to complete, which is equivalent to around 53 days of normal power consumed in an average American household which translates to an average of $200 in cost for a single transaction at 13 cents per kWh.
Thus finding the right location with lower electricity costs of less than 10 cents per kWh will help maintain a profitable bitcoin mining venture.
Profit From Bitcoin Mining
In essence, earnings from bitcoin mining should be able to recover the cost of the mining requirements purchased as well as the running costs of electricity. This is possible with efficient hardware, lower electricity costs, and joining a reliable mining pool which we shall see below.
Is Bitcoin Mining Legal?
No and Yes.
Even though bitcoin has gained wide acceptance across the globe, it still remains highly contested in some countries because of its decentralized nature and volatility and its exorbitantly high power consumption.
In countries like China, Russia, Bolivia, Algeria, and Ecuador, bitcoin trading is either restricted or outright illegal thanks to its decentralized nature, volatile value, association with criminal activities, and several other reasons. In other countries, the legal status of bitcoin is unknown.
EU countries like Finland, Germany, France, and others as well as the United States, Canada, Australia, and the UAE, welcome bitcoin and is widely transacted.


